Empowering Autonomous Driving with High-Performance AI Controllers
Challenges and requirements
As autonomous vehicles become more prevalent, the need for controllers that can process vast data from sensors, cameras, and LiDAR systems in real-time is increasing. These controllers must efficiently execute AI algorithms to ensure accurate decision-making, navigation, and safety while enabling seamless communication between vehicle components. A rugged, reliable design for long-term, uninterrupted operation is also essential. The market's drive for smarter, safer, and more efficient transportation solutions underscores the crucial role autonomous driving controllers play in advancing technology and meeting the demands of modern mobility.
In summary, the key requirements for autonomous driving controllers include:
- High processing power for deploying self-driving AI algorithms
- Versatile connectivity to support sensors and control systems
- A rugged, reliable design for long-term operation
Project Implementation
- MIC-770V3W-00A1, Compact Fanless System with Intel® Core™ CPU Socket (LGA 1700)
- MIC-75G20-10B1, GPU i-Module, 1 PCIe x16 + 1 PCIe x4, dual front accessible storage bay
System Description
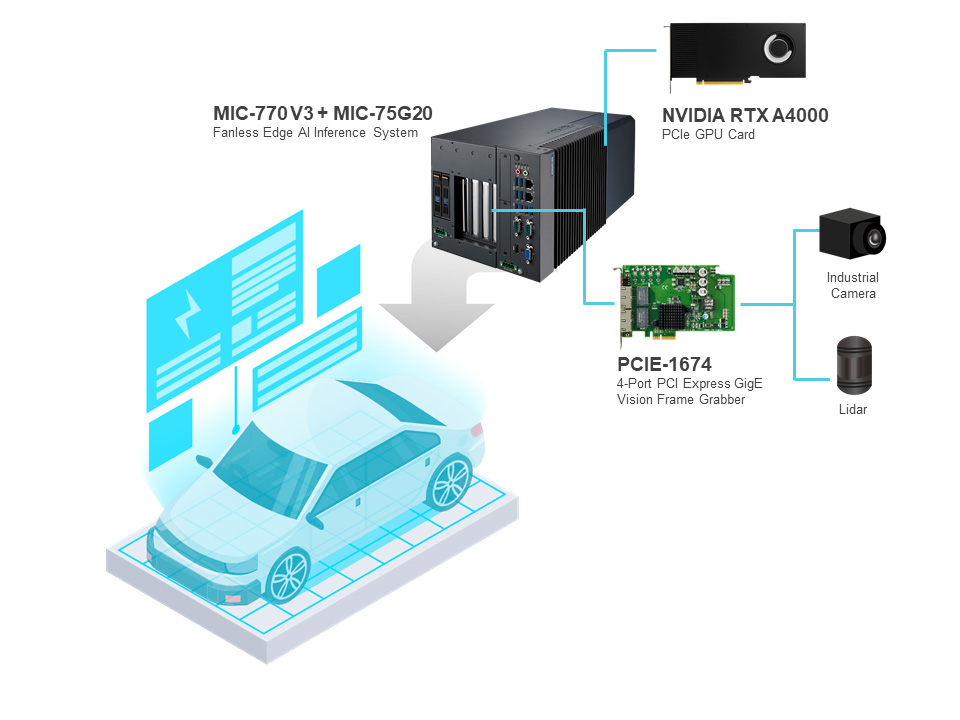
In this case, the autonomous vehicle system operates using a combination of advanced hardware and AI technology to process and analyze data in real time, ensuring smooth, safe navigation. At the core of the system is the MIC-770 V3, a fanless edge AI inference system that acts as the main control unit. Paired with the i-Module MIC-75G20, it supports the integration of additional components, such as a NVIDIA RTX A4000 PCIe GPU card and a PCIE-1674 4-Port PCI Express GigE Vision Frame Grabber.
The NVIDIA RTX A4000 GPU plays a critical role in enhancing system performance by accelerating AI computation and enabling the complex data analysis needed for autonomous driving, including real-time decision-making and AI-driven algorithms for tasks like object detection, lane tracking, and navigation. The PCIE-1674 frame grabber connects with industrial cameras and LiDAR sensors, capturing high-resolution images and 3D spatial data. This data is processed by the GPU, allowing the vehicle to "see" and understand its surroundings, track obstacles, map the environment, and make navigation decisions. The combination of these components ensures that the autonomous vehicle system can handle the vast amounts of data required for safe, efficient, and intelligent autonomous driving operations.
System Diagram